|
|
 ) key or the Down Arrow (
) key or the Down Arrow ( Note: The system automatically assigns RAID level 0 to any logical drives defined in an array containing only one hard disk drive. When this is the case, the Select RAID Level pop-up window will not appear.
If only two hard disk drives are in the array, the Select RAID Level pop-up window appears, but RAID level 5 is not selectable because you need at least three hard disk drives in an array to assign RAID level 5 to one of the logical drives. You can define more than one logical drive for the array. The only restriction is that the maximum number of logical drives you can define is eight, the maximum number of physical drives in an array is 8 or 16, depending on the stripe unit size.
Note:
 ) key or
the Down Arrow (
) key or
the Down Arrow (  )
key to highlight the RAID level you want to assign to these logical
drives,
then press Enter.
)
key to highlight the RAID level you want to assign to these logical
drives,
then press Enter.
Note: Because the level you assign can influence the space needed for the drive, you must assign a RAID level before you enter the size of the logical drive.
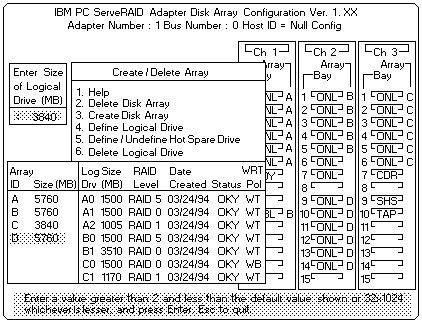
The Logical Drive list contains the logical drive ID, the size of each logical drive, the RAID level you assigned to that logical drive, and the date that the logical drive was created.
The status of the logical drive also is shown. Good means that
OKY means that all is well with the drive.
CRT means that you must replace the hard disk drive or rebuild the logical drive.
(You will have received a message during system startup telling you what has happened to the drive.)
OFL means that the logical drive is irrecoverable, the data on that drive is lost.
If other logical drives have been defined, the Allocation Table appears, showing the logical drive sizes already created, and the amount of free space available.
Information about the new logical drive appears in the Logical Drive list.
Note: The size appearing in the Logical Drive list might be different from the size you typed. (binary equivalent) The size of a logical drive is determined by a number of factors, but basically the size must be divisible by the number of drives in the array.
Consider the following scenarios:
Scenario 1:
The array consists of three 1GB drives.
You assign RAID level 0 (which
uses all the drives in the array with no parity storage), and type
1000MB . The number in the Size (MB) field
will be 999, which is the number closest to and
lower than 1000 that is divisible by 3.
Scenario 2:
The array consists of three 1GB drives, and you assign RAID level 1.
which provides a disk mirroring that stripes data across all drives in the array.
Because the data is mirrored, the capacity of the logical drive is 50% of the physical capacity
of the hard disk drives grouped in the array.
Therefore, if you
type 1000MB , the number in the Size (MB) field
will be 999. The physical capacity used is 2000MB, twice that of the logical drive size.
The number that is closest to or lower than 2000 and is divisible by 3 is 1998. The logical drive size is
999, wich is 50% of the physical capacity.
Scenario 3:
The array consists of three 1GB drives, and you assign RAID level 5. Data is striped across all three drives
in the array, but the space equivalent to that of one drive is used for redundant storage. Therefore, if you
type 1000MB, the number in the Size (MB) field remains 1000 because it is divisable by 2 (drives), which is the space
available for data.
If you do not use the entire array for this logical drive, you can create another by assigning either the same or a different RAID level for an additional logical drive. You can have as many as eight logical drives among eight disk arrays.
 If you select Yes in the Confirm pop-up
window, information in the
logical drive will be overwritten with zeros.
If you select Yes in the Confirm pop-up
window, information in the
logical drive will be overwritten with zeros.
The initialization process begins, and you can see its progress in the Pct. Int. (Percent Initialized) column of the Logical Drive list.
To back up the disk-array configuration:
Follow the instructions on the screen. A pop-up window shows the default file name of CONFIG. You can change the file name by typing over the default. The Backup program will assign a file-name extension of .ips .
Please see the LEGAL - Trademark notice.
Feel free - send a  for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.