|
|
At the adapter level, RAID-5 has become an industry standard method to provide increased availability for servers. RAID-5 and RAID-1 implementations allow servers to continue operation even if there is a 'catastrophic' failure of a hard drive.
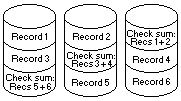
During normal operations in a RAID-5 environment, redundant information is calculated and written out to the drives as shown below. In a n disk environment, n-1 disks of data are provided with one disk of space dedicated to redundant 'check sum' or 'parity' information. The following illustration shows that three 2GB drives provide 4GB of data space and 2GB of redundancy.
For more information refer to:
Please see the LEGAL - Trademark notice.
Feel free - send a  for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.