|
|
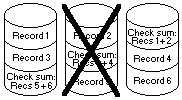
If a drive that is a member of a RAID-5 array fails, the remaining members of the array can use their redundant information to recalculate the lost data, either to respond to user requests for data or to rebuild the data stored on the lost drive when it is replaced with a new one.
In the following illustration, information in Record 1 from Drive 1 is combined with the check sum information on Drive 3 to recreate information that is not available from Drive 2.
Please see the LEGAL - Trademark notice.
Feel free - send a  for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.