|
|
| Identifier | Switch Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 Switches 1, 2, 3, and 4 in combination specify the frequency for the microprocessor. See (below) Table 12 for details. |
| 2 | Switches 1, 2, 3, and 4 in combination specify the frequency for the microprocessor. See (below) Table 12 for details. |
| 3 | Switches 1, 2, 3, and 4 in combination specify the frequency for the microprocessor. See (below) Table 12 for details. |
| 4 | Switches 1, 2, 3, and 4 in combination specify the frequency for the microprocessor. See (below) Table 12 for details. |
| 5 | When On, perform BIOS recovery using boot block (boot block recovery). The recovery boot block is in a protected area of flash memory that cannot be overwritten. When the BIOS becomes corrupted (for example, if a power failure occurs during a flash update), the recovery boot block can be used to restore the BIOS. The code in the recovery boot block enables the server to start up and read a flash diskette. The flash utility automatically recovers the system BIOS from the BIOS recovery files on the diskette. When the flash is complete, the switch must be moved to the Off position. The default setting is Off (disabled). |
| 6 | When On, sets the host bus speed to 66 MHz. When Off, the host bus speed is 100 MHz. The default setting is Off. |
| 7 | Power-on override. When On, overrides the power-on switch and forces power-on mode. The system will always boot without the use of the power-on switch. The default setting is Off (disabled). |
| 8 | When On, bypass the power-on password. When Off, require the user to enter the power-on password at startup if one is set. The default setting is Off. |
NOTE: If the processor in the system does not react to switch changes, it is not an error.
Table 12. Switch Settings for Microprocessor Speed
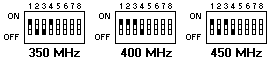
Please see the LEGAL - Trademark notice.
Feel free - send a  for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.