Join a Virtual LAN
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical grouping
of network devices put together as a LAN regardless of their
physical grouping or collision domains. VLANs let a user see and
access only specified network segments. This increases network
performance and improves network security.
VLANs offer the ability to group users and
stations together into logical workgroups. This can simplify
network administration when connecting clients to servers that
are geographically dispersed across the building, campus, or
enterprise network.
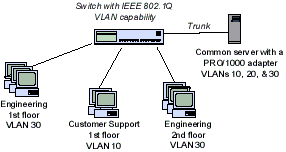
Typically, VLANs consist of co-workers
within the same department but in different locations, groups of
users running the same network protocol, or a cross-functional
team working on a joint project. Joining workers with VLANs forms
logical working groups.
Normally, VLANs are configured at the switch. To set up VLAN membership, your adapter must
be connected to a switch with IEEE 802.1Q VLAN capability.
General Configuration Notes
- VLANs require Windows 2000 or Windows NT 4.0 with Service
Pack 5.0 (or later), or NetWare 4.x and above. VLANs can also be configured under UnixWare* 7.1.x.
- 802.1p/802.1q is required for VLANs to function. You can
enable this feature through the PROSet II's Advanced tab in Windows.
- PRO/100 adapters only support VLANs configured in
compliance with the IEEE 802.1q specification. No support
for ISL (Inter-Switch Link) VLANs is intended.
- When configuring VLANs, make sure the number of VLANs on the server
match the number of VLANs on the switch. A mismatch will cause a Windows Event Log
error to be generated.
Join a VLAN from Windows 2000 or NT 4.0
 |
IMPORTANT: You must use
PROSet to add or remove a VLAN in Windows 2000. Do not
use the Network and Dial-up Connections dialog box to
enable or disable VLANs. Otherwise, the VLAN driver may
not be correctly enabled or disabled. Note that you cannot re-enable a
VLAN in Windows 2000 once it has been disabled. The server must be
restarted to re-enable the connection. |
- Create a VLAN on the switch. Use the parameters you
assign there to join the VLAN from the server. See your switch documentation
for more information.
- Double-click the Intel PROSet icon in Control Panel or
in the system tray.
- Select the adapter you want to be on a VLAN and right click on it.
- In the menu that appears, click Add VLAN. You may see a dialog regarding
802.1 tagging. This tagging must be enabled for VLAN support.
- Enter the VLAN ID and VLAN Name. The VLAN ID must match
the VLAN ID on the switch. Valid ID range is from 1-4094. The VLAN Name is
for informational purposes only and doesn't have to match the name on the
switch.
- Click OK. Repeat steps 3-5 for each VLAN you
want the server to join.
Join a VLAN in NetWare
NetWare versions 4.x and 5.x support VLANs. To join a VLAN
in NetWare applications, you'll need to update your AUTOEXEX.NCF file with LOAD
IANS commands.
See the Examples File
for detailed instructions on configuring VLANs.
General Configuration Notes
- Even if you have a single adapter set up for VLANs, it is called a team.
- VLAN switches must meet IEEE
specifications.
- The same version of iANS should be used for all adapters.
- Always bind iANS to the base driver, and the protocol(s)
to iANS.
Join a VLAN in UnixWare 7.1.x
See Installing the eeE DDI8 Driver for UnixWare* 7 for
instructions on configuring virtual adapters, teaming, and VLANs in UnixWare
7.1.x.

